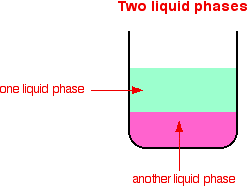
Oil embargo Main Chemical Reactions in FischerTropsch Synthesis Simplified diagram of the RWGS reaction Water gas shift mechanism co e I Sco co C02 co co Sco co co co co oc co co co H— H c HO e CO H C02 112Coordinate Diagrams & Mechanisms Catalysts • SPEED up a reaction without being USED UP in the reaction • ENZYMES are BIOLOGICAL catalysts • HOMOGENOUS Catalysts are in the SAME PHASE as the reactants • HETEROGENEOUS Catalysts are inIn chemistry, heterogeneous catalysis is catalysis where the phase of catalysts differs from that of the reactants or productsThe process contrasts with homogeneous catalysis where the reactants, products and catalyst exist in the same phase Phase distinguishes between not only solid, liquid, and gas components, but also immiscible mixtures (eg oil and water), or anywhere
Catalysis
Heterogeneous catalyst diagram
Heterogeneous catalyst diagram-Heterogeneous Catalysis Fundamentals, Engineering and Characterizations provides a comprehensive introduction to the theory of heterogenous catalysis, including thermodynamic and kinetic aspects, adsorption mechanisms, catalytic reactors and catalyst characterization, with an introduction to sustainable catalysis Representing a reference source for students andFigure 1 shows a schematic diagram of the kind of model systems studied and which will be addressed in the present review8 There are two classes of model systems one, in which the goal is to represent a disperse supported metal or a mixed A Heterogeneous Catalysis 10



How Do Catalysts Work
A heterogeneous catalyst is a catalyst that is present in a different phase (usually a solid) than the reactants Such catalysts generally function by furnishing an active surface upon which a reaction can occur Gas and liquid phase reactions catalyzed by heterogeneous catalysts occur on the surface of the catalyst rather than within the gasHomogeneous vs heterogeneous catalysis Dr habil Marko Hapke 5 5 Heterogeneous Catalysis Major industrial processes using heterogeneous catalysis Process Catalyst Reactants Products Application HaberBosch process Magnetite (Fe) H 2, N 2 NH 3 Fertiliser, explosives Methanol synthesis Cu/ZnO/Al 2O 3 CO, CO 2, H(b) What is the difference between a homogeneous and a heterogeneous catalyst?(c) Do catalysts affect the overall enthalpy change for a reaction, the activation energy, or both?
a, Freeenergy diagram for selective O–H bond insertion over heterogeneous IrSA catalyst b, Free energy diagram for selective O–H insertion over homogeneous Ir(ttp)COCl catalystA heterogeneous catalyst is a catalyst that is present in a different phase (usually a solid) than the reactants Such catalysts generally function by furnishing an active surface upon which a reaction can occur Gas and liquid phase reactions catalyzed by heterogeneous catalysts occur on the surface of the catalyst rather than within the gasMixing, surface area, and temperature are
This chapter starts by considering the simplest possible potential energy diagrams those that describe the elementary step of adsorption of a single atom or molecule on a surface The dissociation of H 2 over a Cu surface is an example of an elementary surface reaction Other types of elementary surface reactions are also illustrated in theHeterogeneous catalysts are 'high tech' materials, of huge economical and societal stake Density Functional Theory (DFT) of electronic structure in molecules and solids has been playing a growing role in the science behind applied heterogeneous catalysis for the past 25 years, and it is the purpose of this article to explain why and howHeterogeneous catalysis plays a key role in the manufacture of essential products in key areas of agriculture and pharmaceuticals, but also in the production of polymers and numerous essential materials Our understanding of heterogeneous catalysts is advancing rapidly, especially by using the latest characterisation methods on these relatively complex effect materials




Catalysis An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Figure 2 From Encyclopedia Of Life Support Systems Eolss Homogeneous And Heterogeneous Catalysis Semantic Scholar
Catalysis Catalysis Heterogeneous catalysis Many catalytic processes are known in which the catalyst and the reactants are not present in the same phase—that is, state of matter These are known as heterogeneous catalytic reactions They include reactions between gases or liquids or both at the surface of a solid catalyst Since the surface is the place at which the reactionChart and Diagram Slides for PowerPoint Beautifully designed chart and diagram s for PowerPoint with visually stunning graphics and animation effects Our new CrystalGraphics Chart and Diagram Slides for PowerPoint is a collection of over 1000 impressively designed datadriven chart and editable diagram s guaranteed to impress any audienceIn heterogeneous catalysis, the catalyst is in a different phase than the reactants Urea is a product of digestion of proteins and other foods that contain nitrogen It can react with water and acid to form ammonium ions and bicarbonate ions according to the equation below




Complexities In Modeling Of Heterogeneous Catalytic Reactions Sciencedirect




Energy Diagram Of A Model For Heterogeneous Catalytic Reactions The Download Scientific Diagram
Heterogeneous catalysts are chemical catalysts whose physical phase is different from the physical phase of the reactants and/or products that take part in the catalyzed chemical reaction Typically, solid phase heterogeneous catalysts are employed in order to facilitate the chemical reaction between two gaseous reactants Catalysts are of many types, but they can be mainly categorized into two groups as homogeneous catalysts and heterogeneous catalysts The key difference between homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysts is that homogeneous catalysts can always be found in the liquid phase whereas heterogeneous catalysts can be found in all three phases of matterComparison of heterogeneous and homogeneous catalysis Necessity is the Mother of Invention WWII;




Elucidation Of Nanostructures In Practical Heterogeneous Catalysts



Frontiers The Advances In The Special Microwave Effects Of The Heterogeneous Catalytic Reactions Chemistry
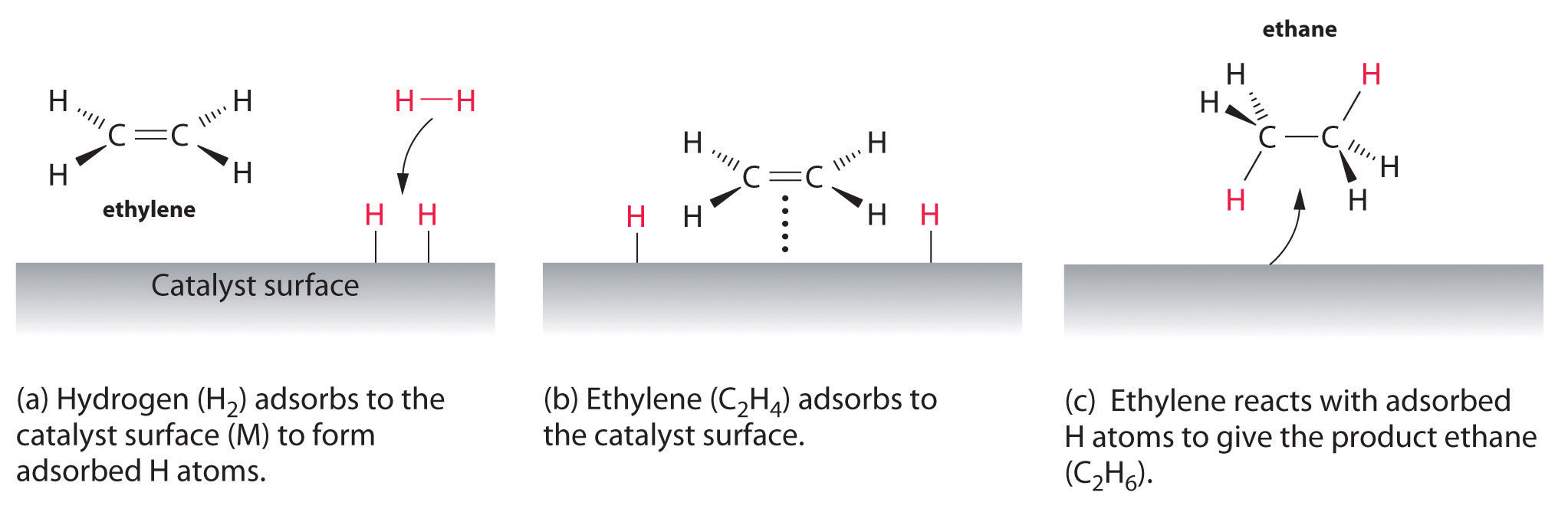
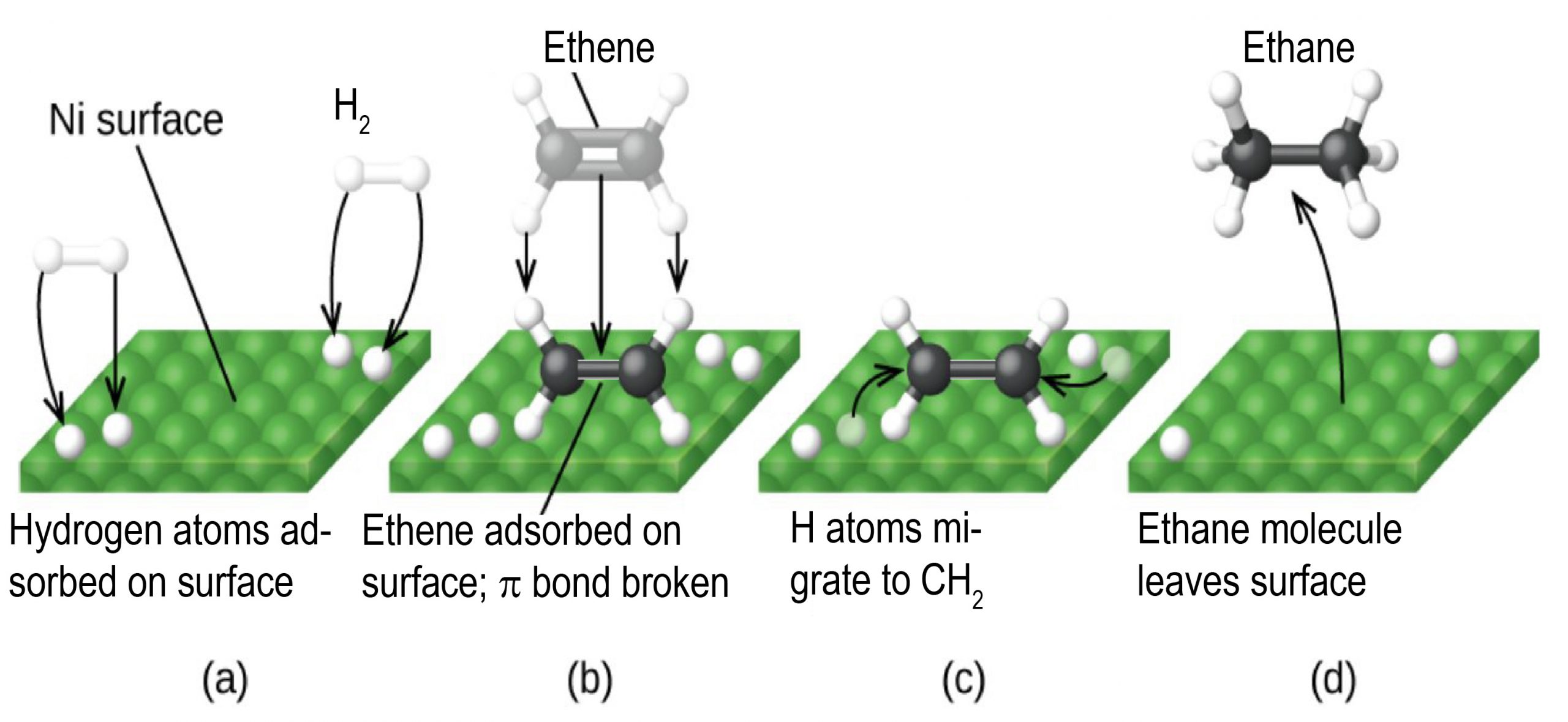
An example of heterogeneous catalysis is the interaction of hydrogen gas with the surface of a metal, such as Ni, Pd, or Pt As shown in part (a) in Figure 1427 "Hydrogenation of Ethylene on a Heterogeneous Catalyst", the hydrogen–hydrogen bonds break and produce individual adsorbed hydrogen atoms on the surface of the metalDownload Applied Heterogeneous Catalysis Design, Manufacture, and Use of Solid Catalysts By J F Le Page – This reference book explains the scientific principles of heterogeneous catalysis while also providing details on the methods used to develop commercially The students should be able to find and choose relevant work from the research literature on a given subject within heterogeneousExamples of Heterogeneous Catalysis and Catalysts – 1 In Haber's process of formation of ammonia, nitrogen and hydrogen are used in gaseous forms while catalyst iron is used in solid form N 2 ( g) 3 H 2 ( g) Fe₍ₛ₎ → Fe₍ₛ₎ 2NH₃ 2




Recent Developments Of Heterogeneous Catalysts For Hydrogenation Of Carboxylic Acids To Their Corresponding Alcohols Tamura Asian Journal Of Organic Chemistry Wiley Online Library




Homogeneous Catalysis Wikipedia
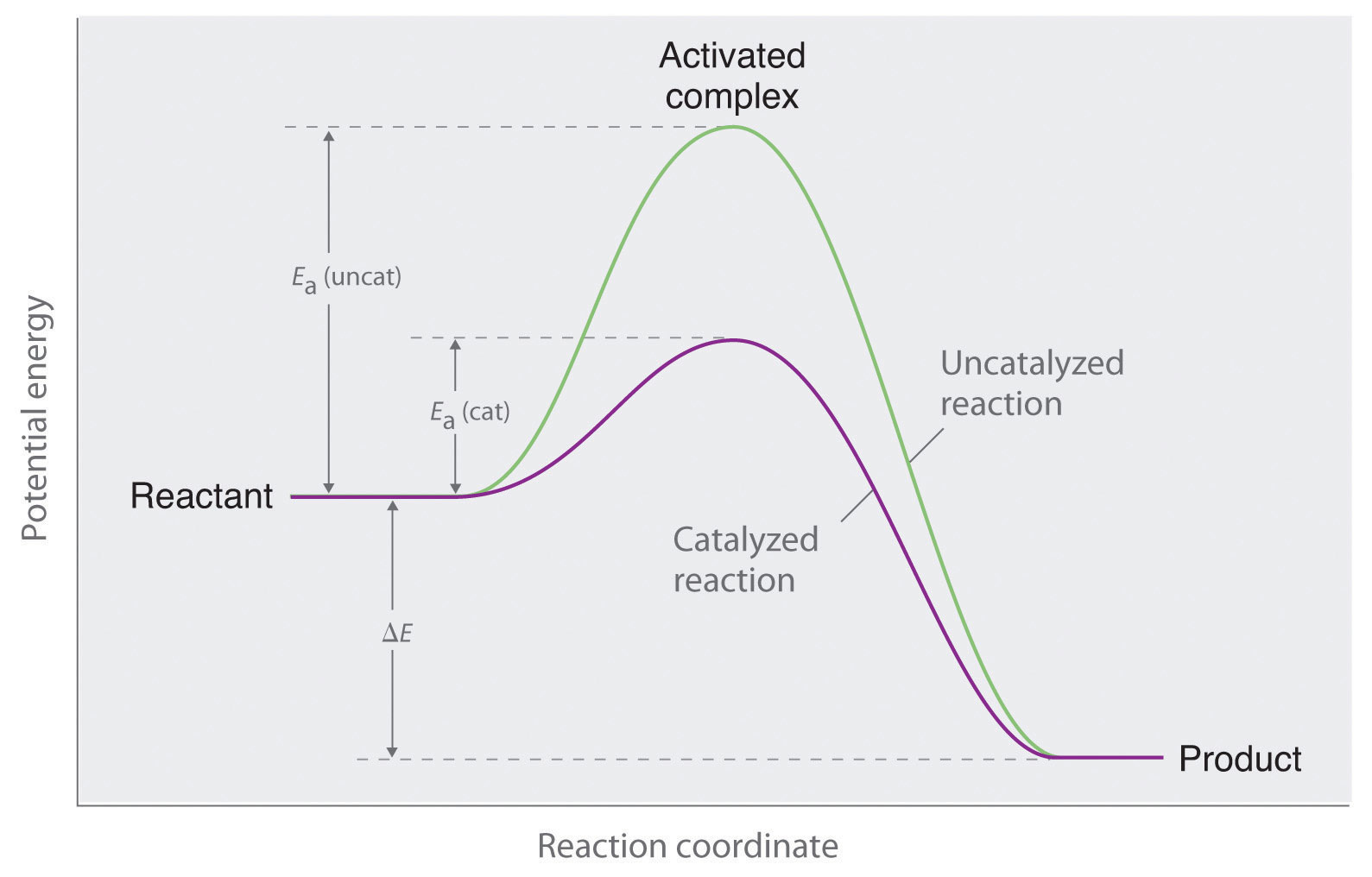
It's time to learn a little more about a chemical reaction How do molecules have to be arranged and how much energy do they have to collide with?Heterogeneous means that the catalyst is in a different phase to the reactants For example, the reactants are gases but the catalyst used is a solid The diagram shows that the catalyst speeds up a reaction that would normally be slow due to the high activation energySurfacescience investigations have contributed significantly to heterogeneous catalysis in the past several decades Fundamental studies of reactive systems on metal single crystals have aided researchers in understanding the effect of surface structure on catalyst reactivity and selectivity for a number of important reactions Recently, model systems, consisting of metal clusters




Catalysis Heterogeneous Catalysis Britannica




Heterogeneous Metal Catalysts For Oxidation Reactions
The diagram above illustrates a typical heterogeneous catalysis eg hydrogenation of alkenes with hydrogen and a nickel catalyst The strength of adsorption is crucial to having a 'fruitful' catalyst surface,HETEROGENEOUS CATALYSIS Prof Shawky M Hassan Professor of Physical Chemistry Contents Chapter 2 Active sites of Heterogeneous Catalysis Chapter 3 Multiplet Theory 31 Geometric Factor 32 Energy Factor Chapter 4 Electronic Theory Chapter 5A heterogeneous catalyst is a catalyst that is present in a different phase (usually a solid) than the reactants Such catalysts generally function by furnishing an active surface upon which a reaction can occur Gas and liquid phase reactions catalyzed by heterogeneous catalysts occur on the surface of the catalyst rather than within the gas




Catalysis Boundless Chemistry




Solid Phase Catalysis In Continuous Flow Syrris Chemistry Blog
Catalysis (/ k ə ˈ t æ l ə s ɪ s /) is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (/ ˈ k æ t əl ɪ s t /)Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after it If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recycles quickly, very small amounts of catalyst often suffice;Schematic energy diagram for the oxidation of CO and a Pt catalyst (From data presented by G Ertl in Catalysis Science and Technology, J R Anderson and M Boudart, Eds, vol 4, SpringerVerlag,Berlin, 19, p 245) All energies are given in kJ molIFor comparison, the heavy dashed lines show a noncatalytic route dioxygen onto the catalystThe choices of alcohols used are mainly methanol, ethanol and butanol The catalysts used in the trans esterification include sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide, sulphuric acid supercritical fluids or enzymes such as lipases1,3,4 Fig 2 Block diagram of
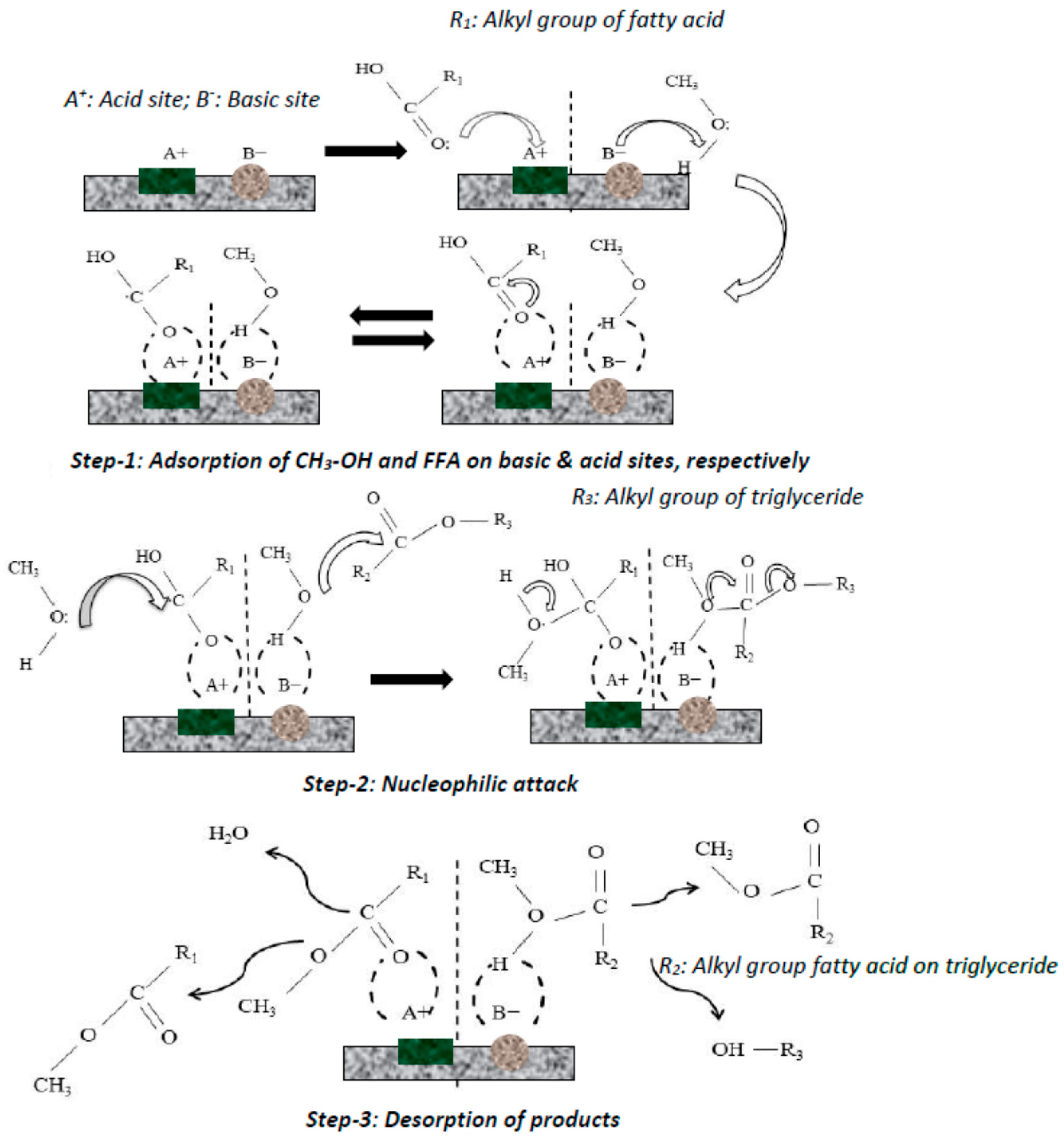



Catalysts Free Full Text Application Of Heterogeneous Catalysts For Biodiesel Production From Microalgal Oil A Review Html




Heterogeneous Catalysis And Electrocatalysis Tests Of The Catalysts A Download Scientific Diagram
2 Heterogeneous Catalysts In heterogeneous catalysis reaction, the catalysts and reactants exist in different phases In reality, the vast majority of heterogeneous catalysts are solids and the vast majority of reactants are either gases or liquids A phase separation catalysis reaction greatly helps in reactant, product, and catalyst separation at the end of the reactionHeterogeneous Catalysis Heterogeneous catalysis has always been a preferred mode of operation for industrial reactors, especially for a reaction like WGS in which homogeneous catalysis implies the use of a multiphase gasliquid reactor with requirements of efficient contactors and liquidliquid separation units for the recovery of the spent catalystA reaction catalysed by a heterogeneous catalyst can be represented by a flow chart and animated diagram Step 1 reactant catalyst Step 2 reactant/catalyst complex Step 3 product/catalyst complex Step 4 product catalyst Making and breaking bonds Reactant molecules are adsorbed at active sites onto the surface of the



Sabatier Principle Wikipedia




Speeding Up Heterogeneous Catalysis With An Improved Highly Reusable Catalyst For The Preparation Of Enantioenriched Secondary Alcohols Sciencedirect
In heterogeneous catalysis, the reactants adsorb onto binding sites on the surface of the catalyst, and the availability of these reaction sites can limit the rate of heterogeneous reactions Key Terms catalyst A substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without being consumed in the processStart studying Heterogeneous catalyst in chemical process Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study toolsA heterogeneous catalyst is a catalyst that is present in a different phase (usually a solid) than the reactants Such catalysts generally function by furnishing an active surface upon which a reaction can occur Gas and liquid phase reactions catalyzed by heterogeneous catalysts occur on the surface of the catalyst rather than within the gas
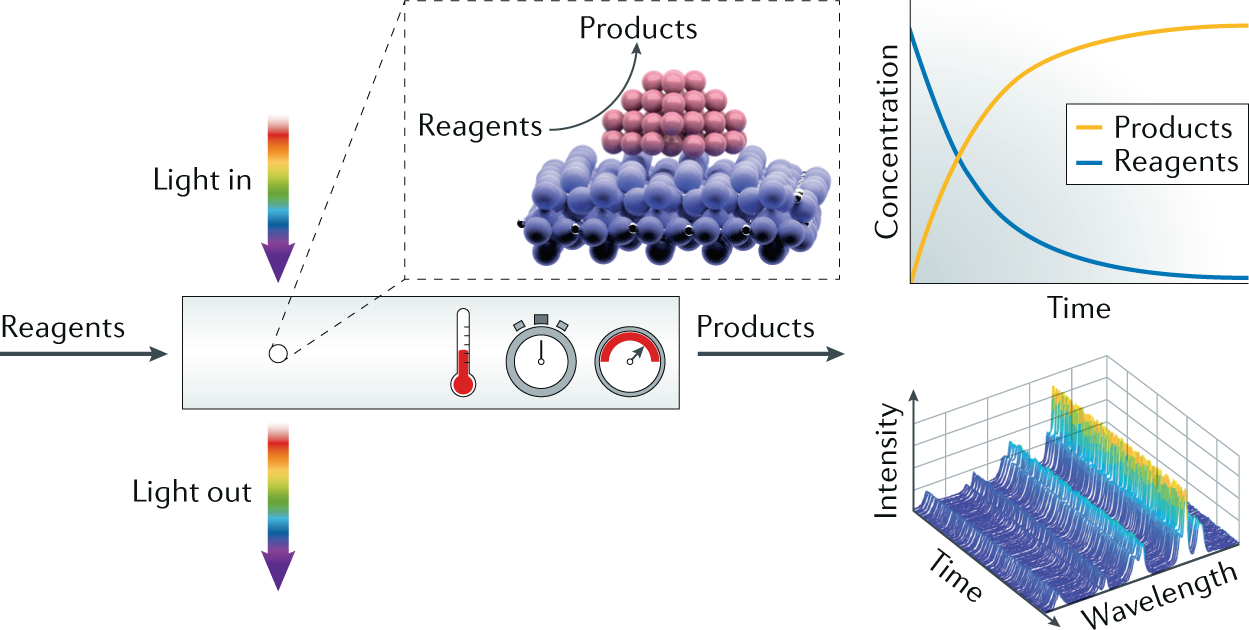



Spatial And Temporal Exploration Of Heterogeneous Catalysts With Synchrotron Radiation Nature Reviews Materials




Adsorption Theory Of Heterogeneous Catalysis Youtube
A heterogeneous catalyst generally has the reaction occurring on the surface of the catalyst, at the phase between the reactants and catalysts Catalysts can be In this section, we will examine the three major classes of catalysts heterogeneous catalysts, homogeneous catalysts, and enzymes Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\) Lowering the Activation Energy of a Reaction by a Catalyst This graph compares potential energy diagrams for a singlestep reaction in the presence and absence of a catalyst Heterogeneous catalysts used for catalytic CO 2 conversion into valuable chemicals such as CO, CH 4, C 2 H 4 have been discussed in this review Because CO 2 is thermodynamically very stable, its conversion usually requires a lot of energy, but the production of that energy also emits considerable CO 2




Heterogeneous Catalysis Sciencedirect




Transition Metals Compounds Acting As Catalysis Catalytic Theory Practice Examples Of Homogeneous Ctalysts Heterogeneous Catalysis Gce As Ib A Level Inorganic Chemistry Revision Notes
Heterogeneous Catalysis Steps Now, as per the modern adsorption theory, which is a combination of the old theory of adsorption and the intermediate theory of compound formation, the process of heterogeneous catalysis takes place with these five steps, The reactants diffuse to the surface of the catalysts A heterogeneous catalyst is a catalyst that is present in a different phase (usually a solid) than the reactants Such catalysts generally function by furnishing an active surface upon which a reaction can occur Gas and liquid phase reactions catalyzed by heterogeneous catalysts occur on the surface of the catalyst rather than within the gasCompared to traditional heterogeneous catalysts such as oxides or supported metal particles The heterogeneity of the surface sites is, in fact, a common feature of the heterogeneous catalysts Property Homogeneous Heterogeneous Catalyst recovery difficult and expensive easy and cheap Thermal stability poor good
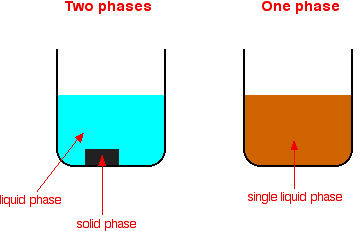



Types Of Catalysis
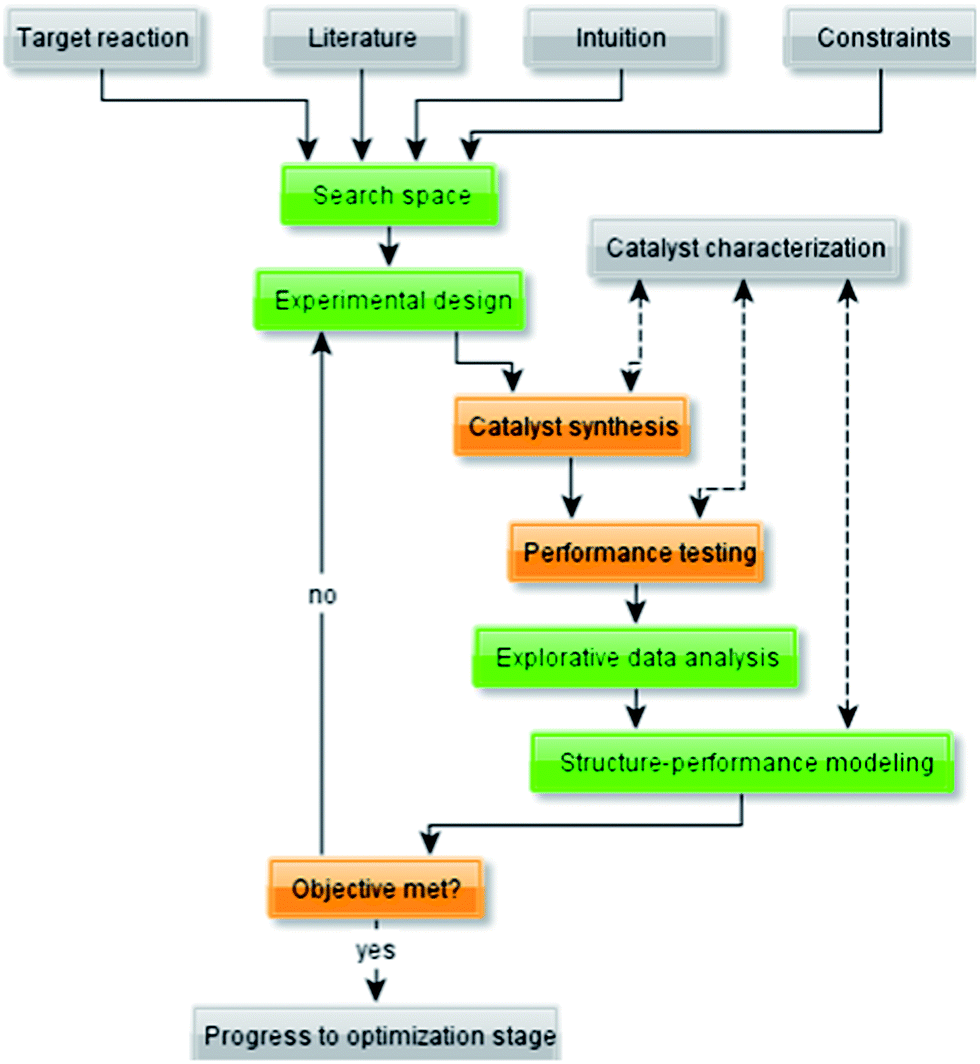



Heterogeneous Catalyst Discovery Using 21st Century Tools A Tutorial Rsc Advances Rsc Publishing Doi 10 1039 C3rak
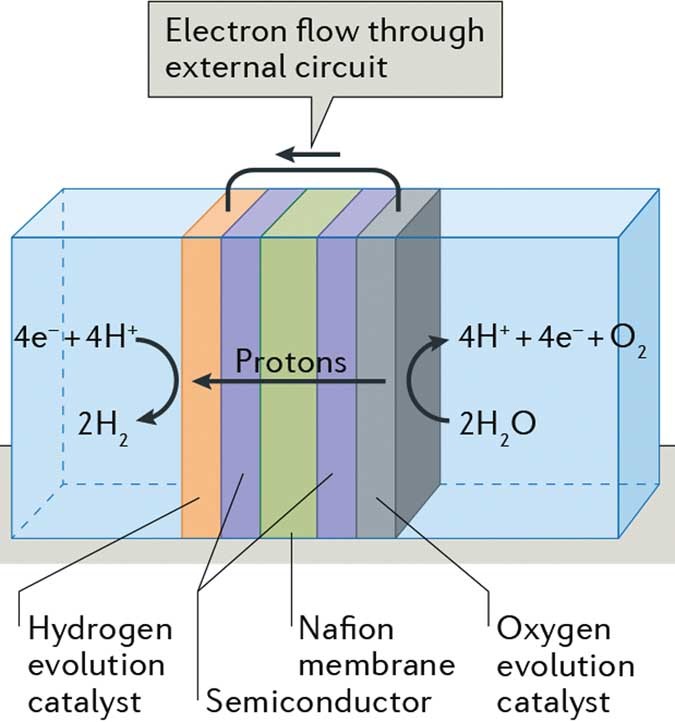
Figure 1 Schematic diagrams of four different schemes for lightassisted CO2 reduction on a semiconducting photocathode (a) heterogeneous catalysis on a semiconductor electrode, (b) heterogeneous caCharacterization is a central aspect of catalyst development 1,2 The elucidation of the struc ture, composition, and chemical properties of both the solids used in heterogeneous catalysis 4 Heterogeneous involves more than one phase usually the catalyst is a solid and the reactants and products are in liquid or gaseous form A heterogeneous catalytic reaction occurs at or very near the fluidsolid interface Reactions between gases




Differences Between Homogeneous Catalysis And Heterogeneous Catalysis Qs Study




Heterogeneous Catalysis Wikipedia
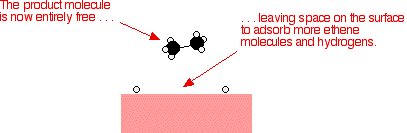
How the heterogeneous catalyst works (in general terms) Most examples of heterogeneous catalysis go through the same stages One or more of the reactants are adsorbed on to the surface of the catalyst at active sites Adsorption is where something sticks to a surfaceIt isn't the same as absorption where one substance is taken up within the structure of anotherMechanism Description A number of heterogeneous solid catalysts have been reported to cleave BOC groups These are mostly sulfonated resins in their acid forms, although other solids have been reported to cleave BOC groupsThe reaction is probably catalyzed by acidic sites on the solid surface, so all heterogeneous catalysts most likely follow the acid cleavage mechanism (a) What is a catalyst?




Energy Reaction Path For Heterogeneous And Homogeneous Reaction Download Scientific Diagram
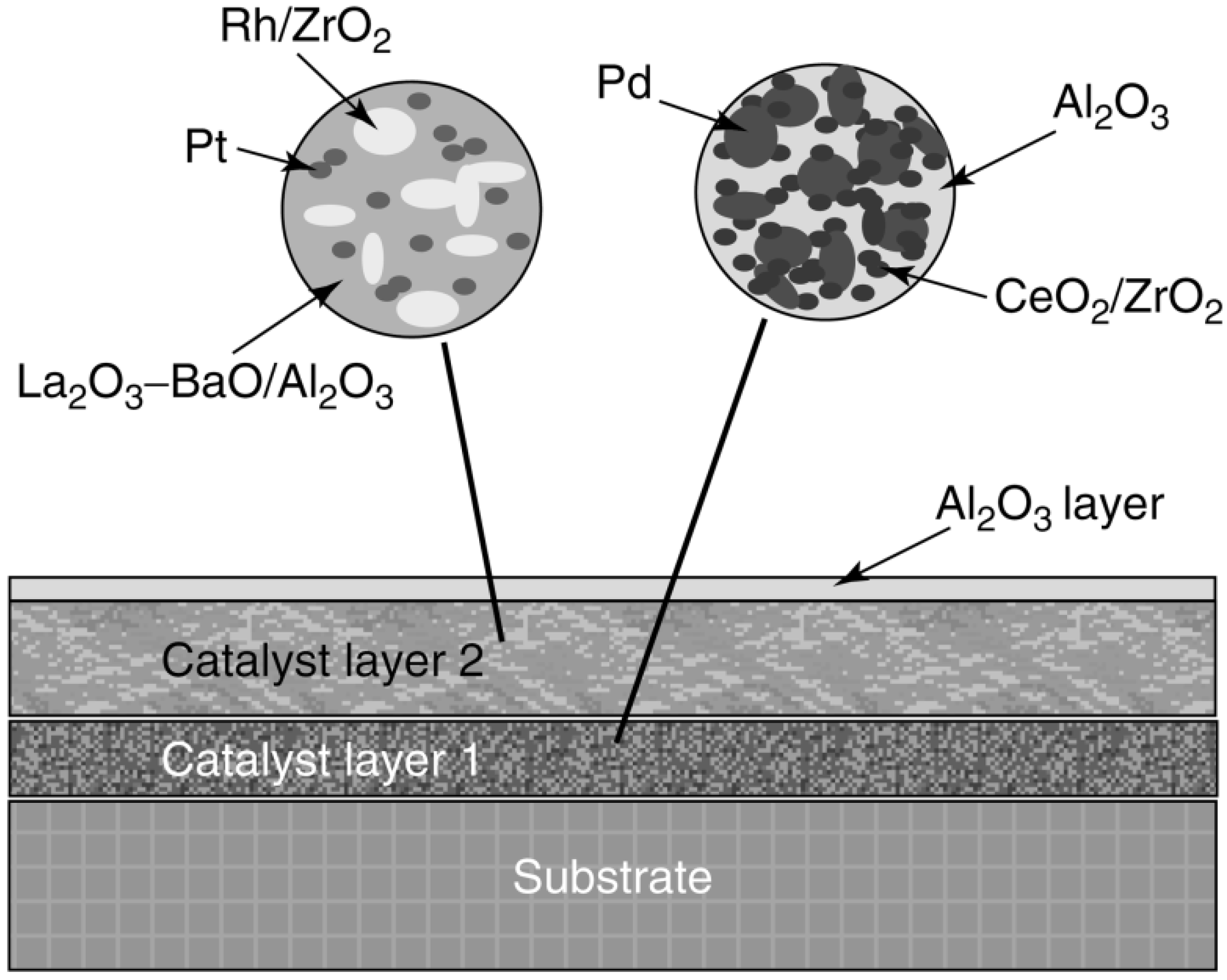



Catalysts Free Full Text Heterogeneous Catalyst Deactivation And Regeneration A Review Html
Heterogeneous Catalysts A strategy for minimising metal levels in products is to use heterogeneous/supported catalysts These catalyst types also facilitate recovery, reuse and recycling as well as being amenable to use in flow reactions Historically, metals on carbon developed as hydrogenation catalysts were used, but many more sophisticatedThe development of descriptor performance relationships for heterogeneous catalysts is hampered by the fact that the active site of a heterogeneous complex is often poorly defined In contrast, in homogeneous catalysis the entire catalyst is a well defined, molecular complex that can readily be described by common computational chemistry software



Catalytic Activity



Catalysis Introductory Chemistry




Crossing The Divide Between Homogeneous And Heterogeneous Catalysis In Water Oxidation Pnas




Heterogeneous Catalysis Wikipedia
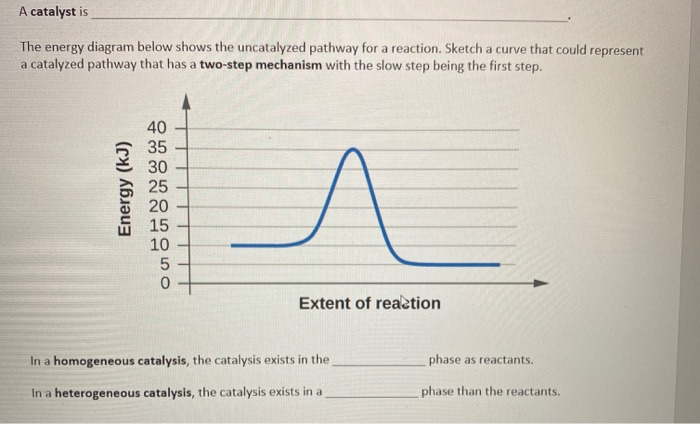



A Catalyst Is The Energy Diagram Below Shows The Chegg Com



Http Www Umich Edu Elements 6e Powerpoints 13lectures Lec27 Pdf Pdf



1




Machine Learning For Heterogeneous Catalyst Design And Discovery Goldsmith 18 Aiche Journal Wiley Online Library



Homogeneous Versus Heterogeneous Catalysis Download Scientific Diagram
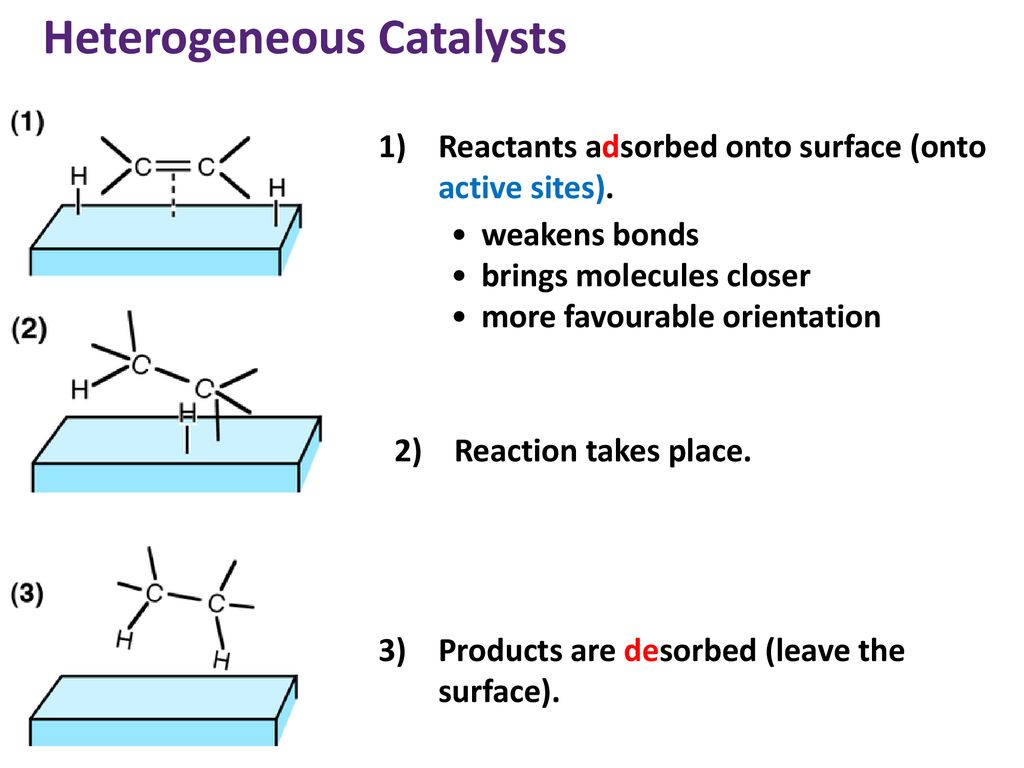



Catalysis Ppt Download



How Do Catalysts Work




Carbon Support Based Heterogeneous Nanocatalysts Synthesis And Applications In Organic Reactions Bahuguna 19 Asian Journal Of Organic Chemistry Wiley Online Library




Homogeneous Catalysis Introduction To Chemistry



Q Tbn And9gctrvbbisy7ikjyh35 8msk3jkudkzizuszlwrim5fn3f2i54ygk Usqp Cau




Heterogeneous Catalyst Stability During Hydrodenitrogenation In Supercritical Water Sciencedirect




Schematic Of The Heterogeneous Catalysis Process On Porous Catalysts Download Scientific Diagram




How To Measure The Reaction Performance Of Heterogeneous Catalytic Reactions Reliably Sciencedirect



Catalysts Free Full Text Heterogeneous Catalysis On Metal Oxides



Sustainable And Recyclable Heterogenous Palladium Catalysts From Rice Husk Derived Biosilicates For Suzuki Miyaura Cross Couplings Aerobic Oxidations And Stereoselective Cascade Carbocyclizations Scientific Reports
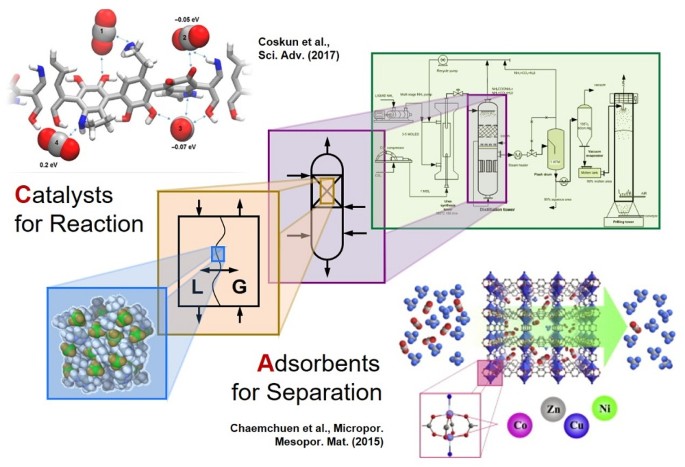



Computational Design Of Heterogeneous Catalysts And Gas Separation Materials For Advanced Chemical Processing Springerlink




Heterogeneous Catalysis Wikipedia



Katz Group Research Chemical Biomolecular Engineering Uc Berkeley
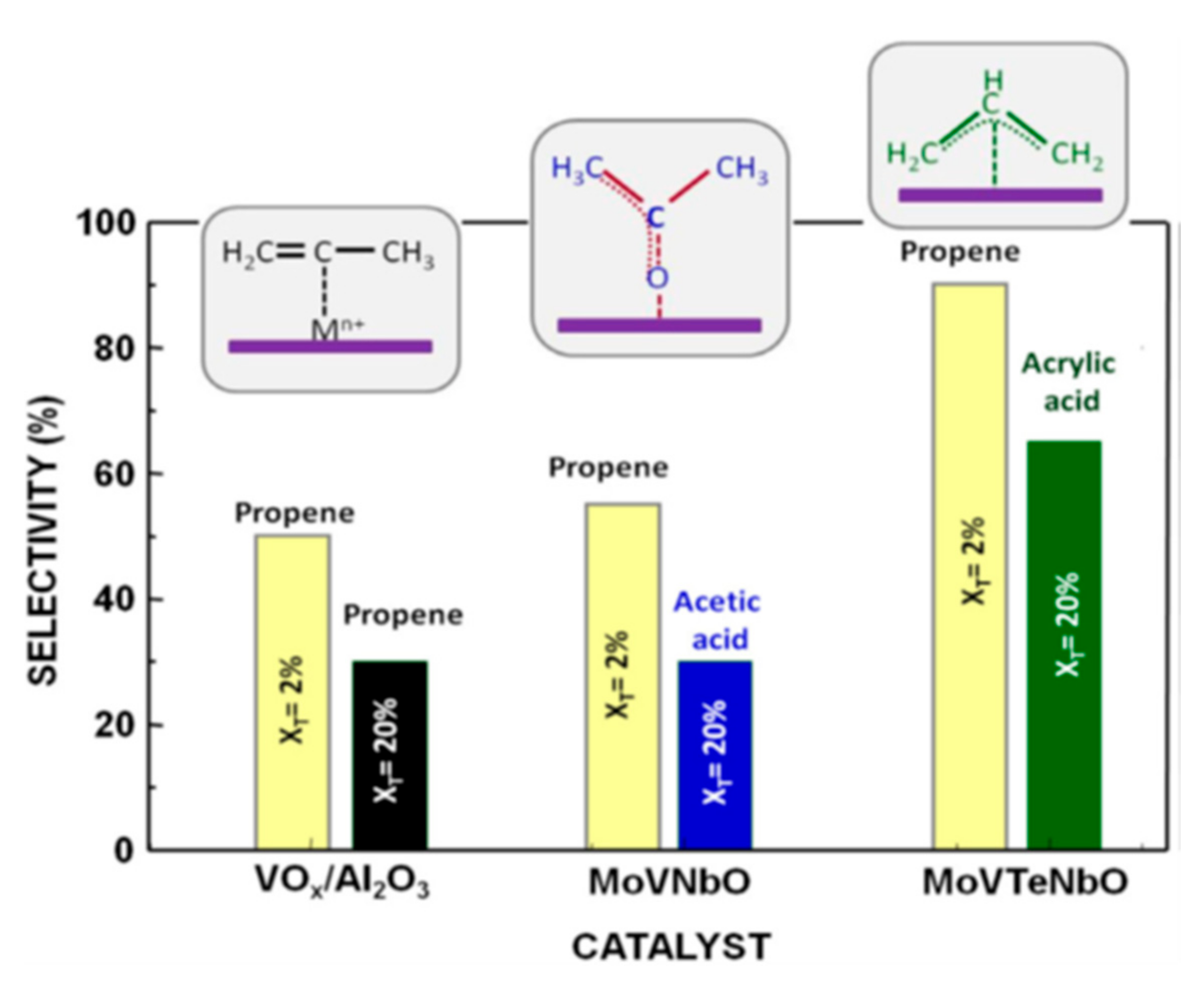



Catalysts Free Full Text Heterogeneous Catalysis On Metal Oxides Html




3 The Mechanisms Of Heterogeneous Catalysts Surface Reactions A Download Scientific Diagram



Direct Arylation Using Heterogeneous Catalysts With Evidence Of Download Scientific Diagram




Kinetic Aspects Of Heterogeneous Catalytic Versus Photocatalytic Reactions Sciencedirect



Catalysis Authorstream




Figure 26 1 From Homogeneous And Heterogeneous Catalysis Semantic Scholar




Kinetics Theory Of Catalytic Mechanisms Heterogeneous Catalysis Homogeneous Catalyzed Reaction Examples Advanced A Level Gce Revision Notes




Catalysis
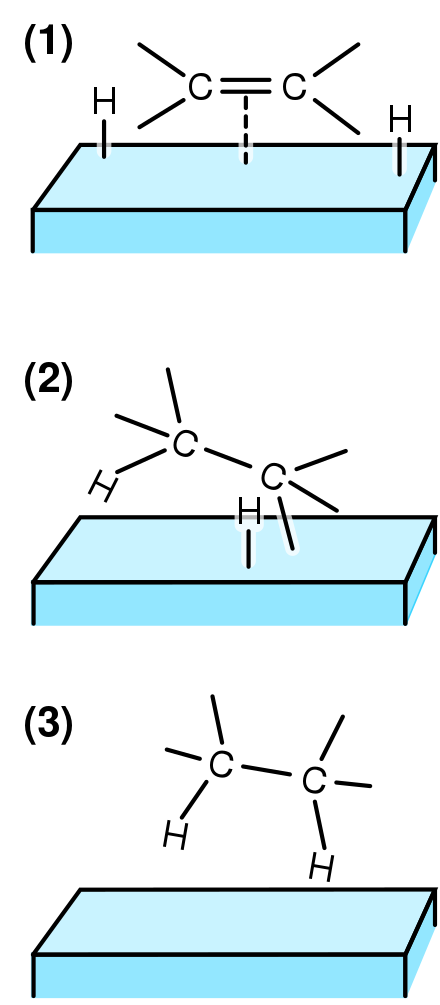



Heterogeneous Catalysis Wikiwand
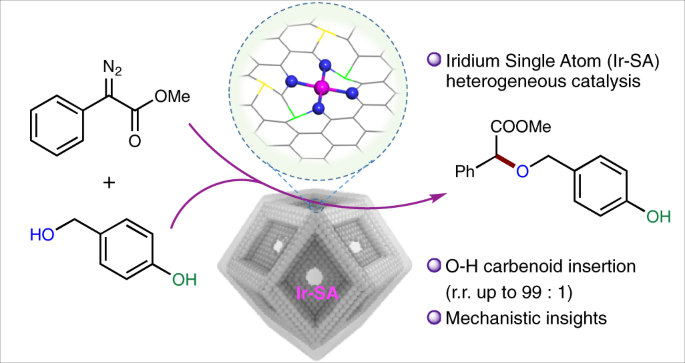



A Heterogeneous Iridium Single Atom Site Catalyst For Highly Regioselective Carbenoid O H Bond Insertion Nature Catalysis




1 Potential Energy Diagram Of A Heterogeneous Catalytic Reaction A B Download Scientific Diagram



Types Of Catalysis



Q Tbn And9gcszztkjbzfsntexsurtvk4nl6npftcvaalxtfswqxoyuadjnltd Usqp Cau



D37 4 Heterogeneous Catalysts Chemistry 109 Fall 21




1 Potential Energy Diagram Of A Heterogeneous Catalytic Reaction A B Download Scientific Diagram



Types Of Catalysis
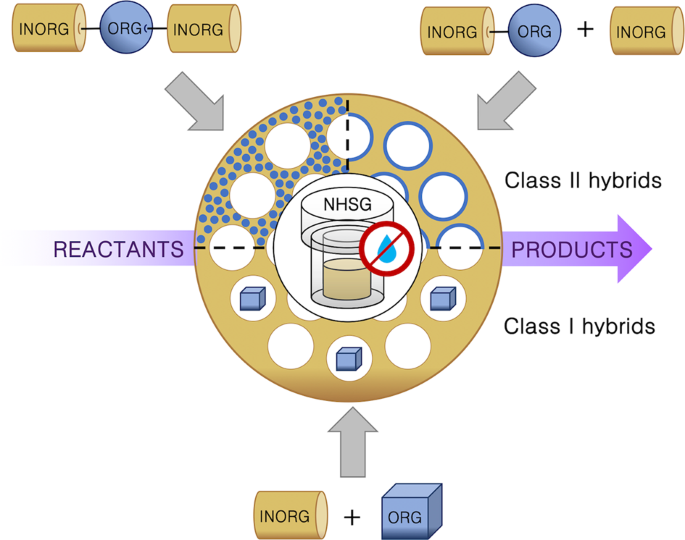



Non Hydrolytic Sol Gel As A Versatile Route For The Preparation Of Hybrid Heterogeneous Catalysts Springerlink



Heterogeneous Catalysis Shatruk Group Florida State University
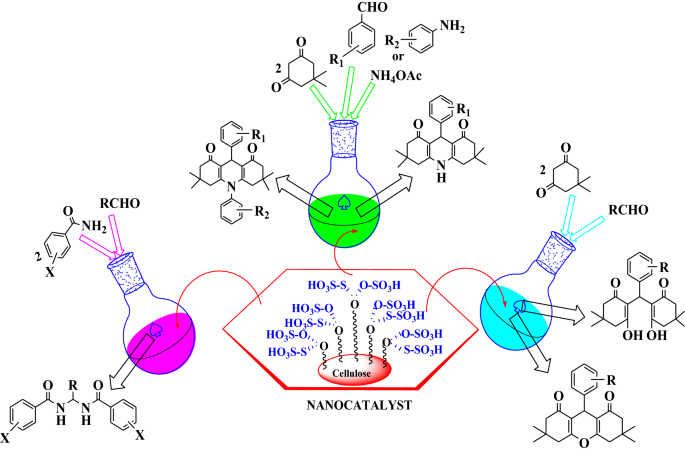



Carbon Based Nanocatalyst An Efficient And Recyclable Heterogeneous Catalyst For One Pot Synthesis Of Gem Bisamides Hexahydroacridine 1 8 Diones And 1 8 Dioxo Octahydroxanthenes Springerlink



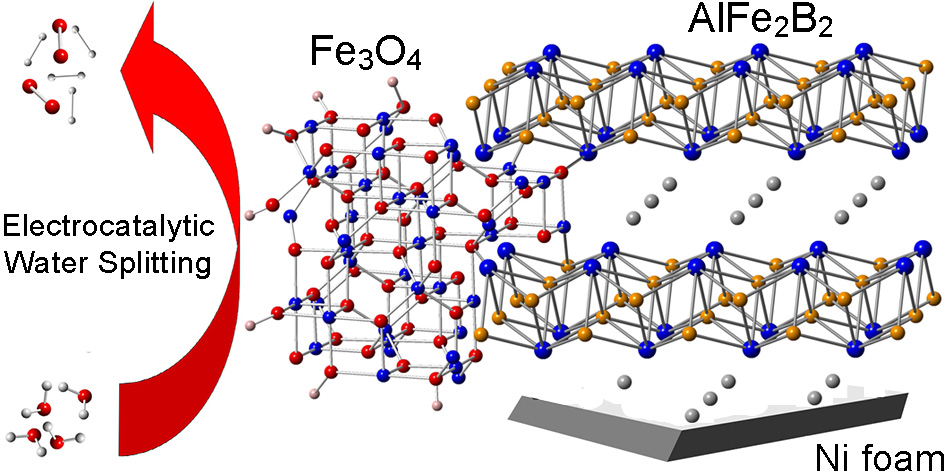
Heterogeneous Catalysis Base Metals Break Up Water Nature Reviews Chemistry




Individual Steps Of A Simple Heterogeneous Catalytic Fluid Solid Download Scientific Diagram
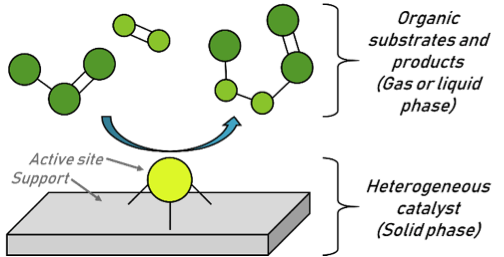



Cook Reu




2 A Potential Energy Diagram Of A Heterogeneous Catalytic Reaction Download Scientific Diagram
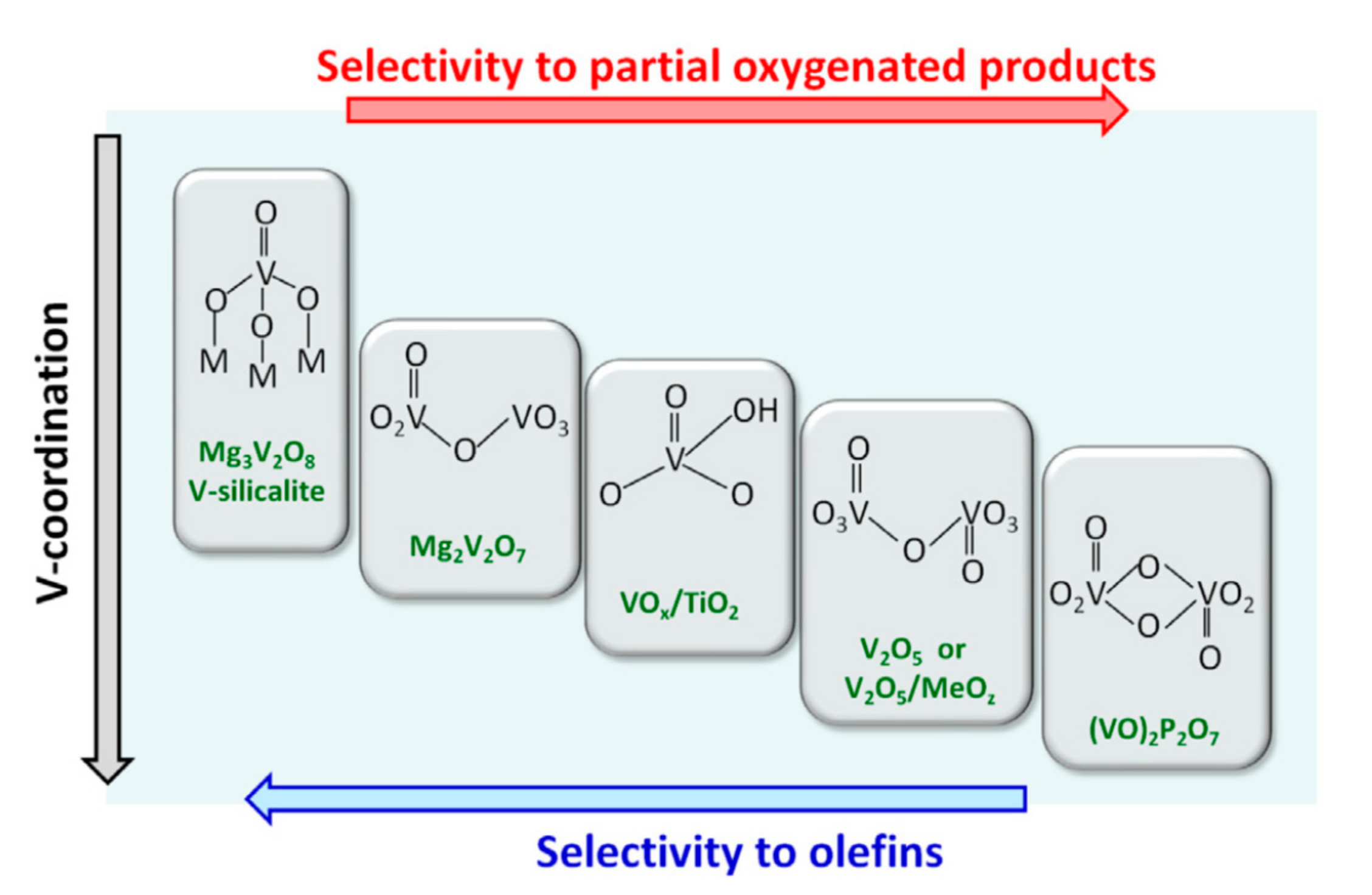



Catalysts Free Full Text Heterogeneous Catalysis On Metal Oxides Html



How Do Catalysts Work




Describe How A Heterogeneous Catalyst Works And Explain The Factors That Determine The Effectiveness Of Such A Catalyst Study Com
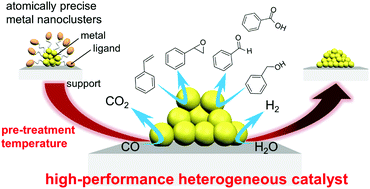



Toward The Creation Of High Performance Heterogeneous Catalysts By Controlled Ligand Desorption From Atomically Precise Metal Nanoclusters Nanoscale Horizons Rsc Publishing




1 Schematic Diagram Of The Reaction Pathes In Homogeneous Download Scientific Diagram
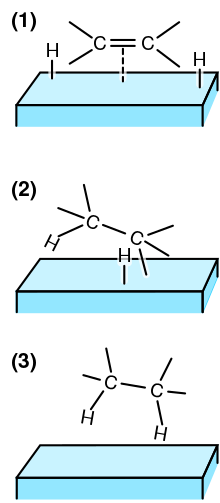



Heterogeneous Catalysis Wikipedia




Heterogeneous Catalysis The Ice Group
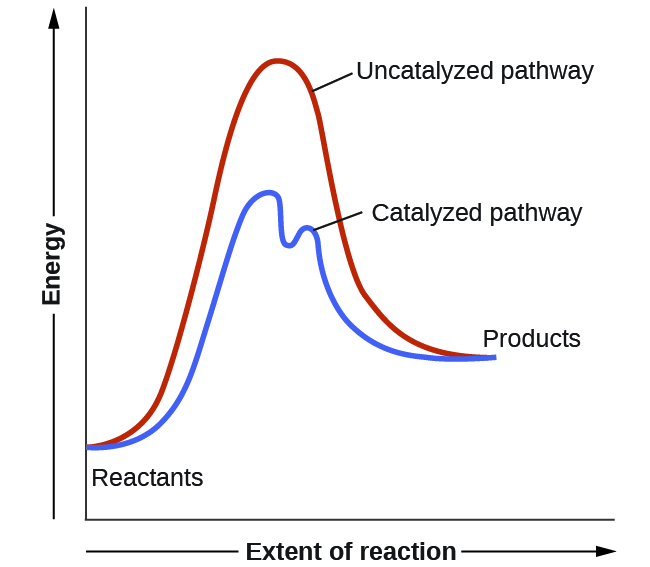



12 7 Catalysis Chemistry 112 Chapters 12 17 Of Openstax General Chemistry
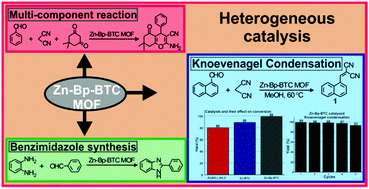



A Zn Based Metal Organic Framework As A Heterogeneous Catalyst For C C Bond Formation Reactions New Journal Of Chemistry Rsc Publishing



Homogeneous Vs Heterogeneous Catalysts Basic Introduction Youtube
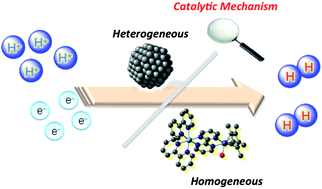



Catalytic Mechanisms Of Hydrogen Evolution With Homogeneous And Heterogeneous Catalysts Energy Environmental Science Rsc Publishing



3




New Trends In The Development Of Heterogeneous Catalysts For Electrochemical Co2 Reduction Sciencedirect
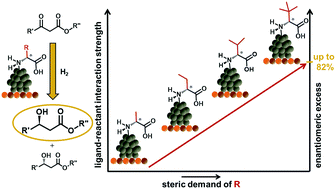



Ligand Functionalized Pt Nanoparticles As Asymmetric Heterogeneous Catalysts Molecular Reaction Control By Ligand Reactant Interactions Catalysis Science Technology Rsc Publishing




Energy Diagram Of A Model For Heterogeneous Catalytic Reactions The Download Scientific Diagram




Types Of Catalysts Article Kinetics Khan Academy




Heterogeneous Catalysis Alchetron The Free Social Encyclopedia
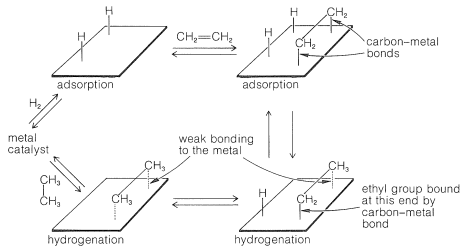



11 2 Hydrogenation With Heterogeneous Catalysts Chemistry Libretexts
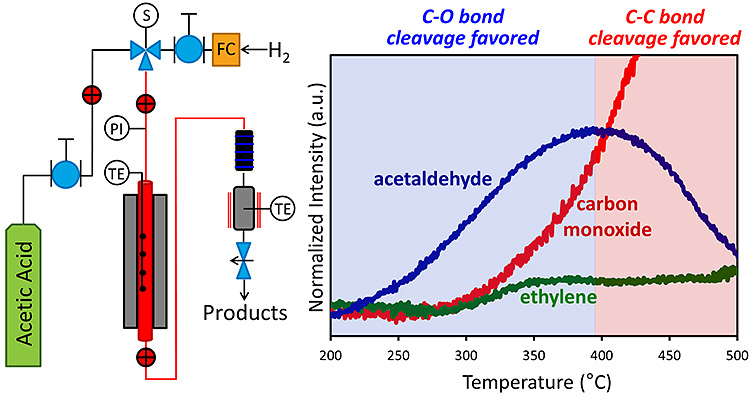



Heterogeneous Catalysis For Thermochemical Conversion Bioenergy Nrel




Heterogeneous Catalysis An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Transition Metals Compounds Acting As Catalysis Catalytic Theory Practice Examples Of Homogeneous Ctalysts Heterogeneous Catalysis Gce As Ib A Level Inorganic Chemistry Revision Notes
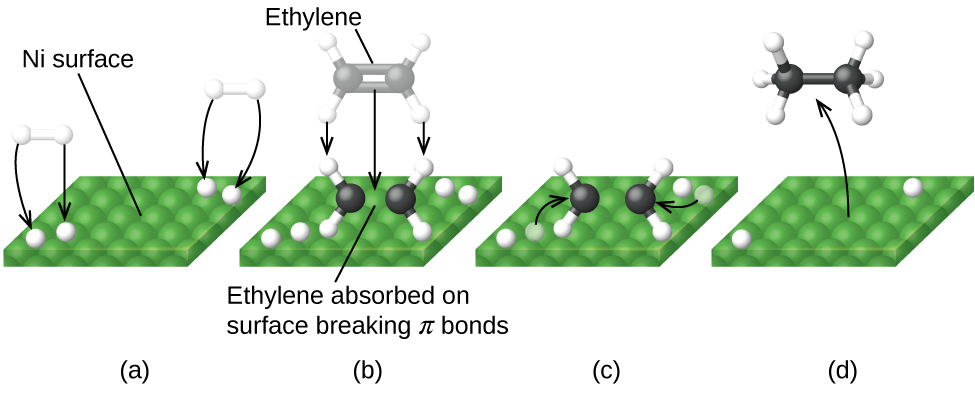



12 7 Catalysis Chemistry Libretexts
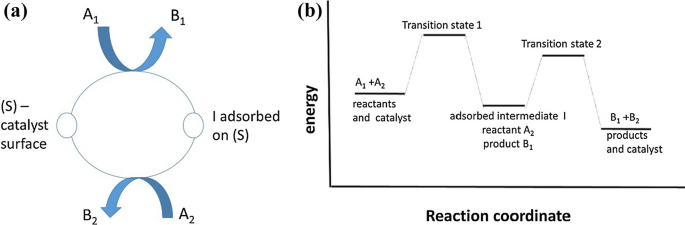



On The Optimum Catalyst For Structure Sensitive Heterogeneous Catalytic Reactions Springerlink



1 An Introduction To Types Of Catalysis Chemistry Libretexts



Catalysis



Http Www Umich Edu Elements 6e Powerpoints 13lectures Lec27 Pdf Pdf



Http Www Fhi Berlin Mpg De Acnew Department Pages Teaching Pages Teaching Wintersemester 16 17 Robert Schloegl Introduction To Heterogeneous Catalysis Pdf




Synthesis Of Amides Functionalized Pops Supported Nano Pd Catalysts For Phosphine Ligand Free Heterogeneous Hydroaminocarbonylation Of Alkynes Wang Advanced Synthesis Amp Catalysis Wiley Online Library
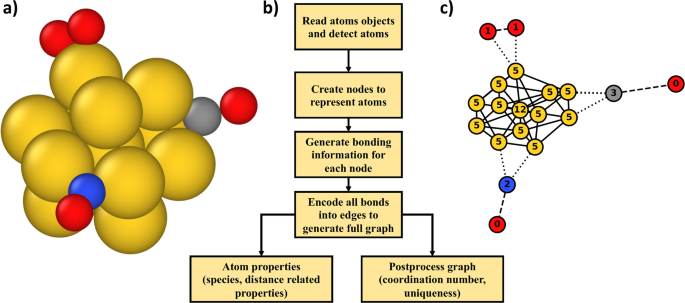



Graph Theory Approach To Determine Configurations Of Multidentate And High Coverage Adsorbates For Heterogeneous Catalysis Npj Computational Materials
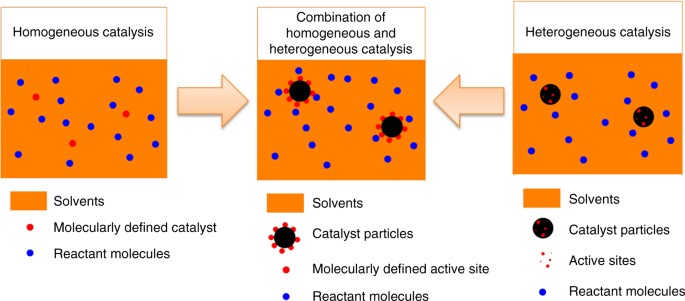



Synthesis Of A Molecularly Defined Single Active Site Heterogeneous Catalyst For Selective Oxidation Of N Heterocycles Nature Communications




Homogeneous Heterogeneous Catalysts Cie A Level Chemistry 19 21 Notes




Solid Phase Catalysis In Continuous Flow Syrris Chemistry Blog



Catalysts Free Full Text Heterogeneous Catalysis On Metal Oxides Html



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿